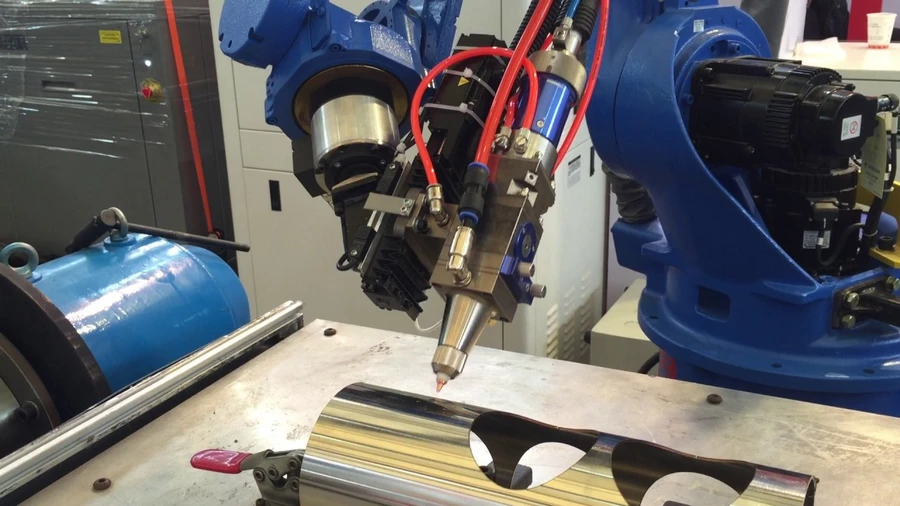

In the vast realm of industrial innovation, where technology meets precision and productivity, there exists a formidable force that has reshaped the way we cut and shape materials. It is a fusion of human ingenuity and machine prowess, a phenomenon that commands attention and instills a sense of wonder. Prepare to embark on a journey into the realm of laser cutting robots.
Imagine a world where beams of focused light dance upon surfaces, effortlessly slicing through metal, wood, and fabrics with unparalleled precision. Such a world is not confined to the realm of science fiction but is a tangible reality forged through the fusion of cutting-edge robotics and the transformative power of lasers.
In this exploration, we shall uncover the intricacies and capabilities of laser cutting robots, revealing the secrets behind their efficiency, the diverse applications they serve, and the advantages they offer over traditional human labor. Brace yourself for a captivating encounter with a technology that blurs the line between science and art, where seemingly impossible shapes come to life with a gentle touch of laser brilliance.
what is a laser cutting robot?
A laser cutting robot, also known as a laser cutter or laser cutting system, is a robotic device equipped with a laser beam that is used to cut or engrave various materials with precision. It combines the capabilities of a robot, which provides automated movement and positioning, with a high-powered laser source for cutting or etching tasks.
The laser cutting robot typically consists of several components. These include:
1. Robotic Arm
The robotic arm is responsible for the movement and positioning of the laser cutting tool. It is usually a multi-axis arm that can be programmed to move the laser head with high accuracy and repeatability.
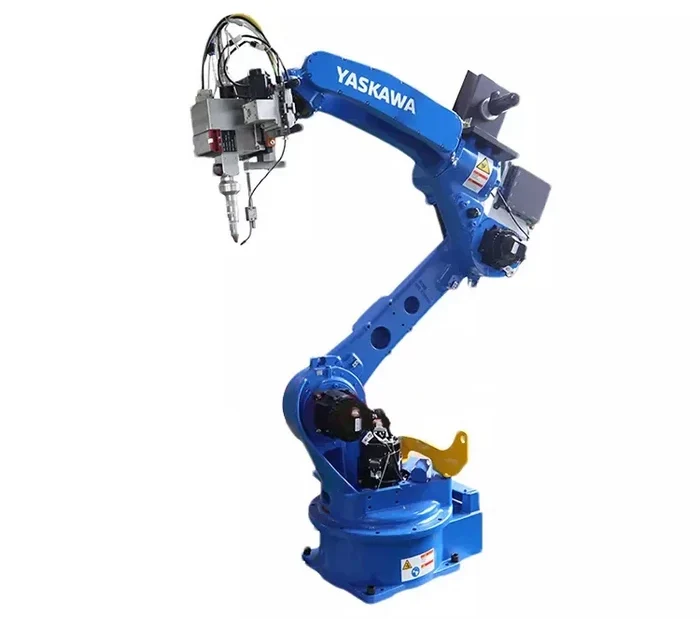

2. Laser Source
The laser source generates a high-intensity laser beam, typically a CO2 or fiber laser, that is focused onto the material being cut. The laser beam is emitted through a nozzle or focusing lens.
3. Cutting Head
The cutting head is attached to the end of the robotic arm and holds the focusing lens or nozzle. It helps to control the focal point of the laser beam and the distance between the material and the lens.
4. Control System
The control system includes the software and hardware that enable programming and operation of the laser cutting robot. It allows users to define the cutting path, control the laser power, and adjust other parameters for the cutting or engraving process.
When the laser cutting robot is activated, the robotic arm moves the cutting head along the predetermined path while the laser beam is emitted. The intense heat from the laser beam melts, vaporizes, or burns away the material, resulting in precise cuts or intricate designs. The robot’s precise movements ensure accurate and repeatable cutting, making it suitable for a wide range of applications, such as industrial manufacturing, prototyping, signage, and artistic creations.
Laser cutting robots offer several advantages, including high cutting speed, minimal material waste, the ability to cut complex shapes, and the versatility to work with various materials like metal, wood, acrylic, fabric, and more. They are widely used in industries that require precision cutting and engraving, offering increased efficiency and automation compared to traditional manual cutting methods.
what are the applications of a laser cutting robot?
A laser cutting robot has a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the common applications include:
1. Industrial Manufacturing
Laser cutting robots are extensively used in industrial manufacturing processes. They can cut and shape various materials like metal sheets, pipes, tubes, and plates with high precision. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and furniture manufacturing rely on laser cutting robots to produce components, parts, and prototypes.
2. Fabrication and Metalworking
Laser cutting robots are widely employed in metalworking and fabrication industries. They can cut intricate patterns, holes, and shapes in metal sheets, tubes, and plates. Laser cutting robots are used for tasks such as cutting sheet metal for HVAC systems, creating structural components, fabricating prototypes, and producing decorative metalwork.
3. Signage and Advertising
Laser cutting robots are ideal for creating precise and intricate designs on various materials, including acrylic, wood, and metal. They are commonly used for producing signage, logos, letters, and decorative elements in the advertising and signage industry. The robots can cut out precise shapes and engrave detailed designs, allowing for customized and eye-catching displays.

4. Art and Design
Laser cutting robots have gained popularity in the art and design world due to their ability to cut and engrave with high precision. Artists and designers utilize laser cutting robots to create intricate sculptures, models, jewelry, and other artistic creations. The robots allow for detailed and complex designs on various materials, including wood, paper, fabric, and acrylic.
5. Textile and Fashion Industry
Laser cutting robots are used in the textile and fashion industry for precise cutting of fabrics. They can cut intricate patterns, appliques, and shapes in fabrics without fraying or distorting the material. Laser cutting technology enables quick and accurate cutting for garment manufacturing, fashion design, and textile prototyping.
6. Medical and Pharmaceutical
Laser cutting robots play a crucial role in the medical and pharmaceutical sectors. They are used for precise cutting and shaping of materials such as surgical instruments, implants, and medical devices. Laser cutting ensures clean edges, minimal thermal damage, and high accuracy, meeting the stringent requirements of the medical industry.
7. Prototyping and Rapid Manufacturing
Laser cutting robots are often employed in rapid prototyping and small-scale manufacturing. They enable quick and precise fabrication of prototypes, reducing development time and costs. Laser cutting robots can transform digital designs into physical objects with high accuracy and repeatability.
These are just a few examples of the applications of laser cutting robots. The versatility, precision, and automation offered by these robots make them valuable tools in a wide range of industries where precise cutting, shaping, and engraving are required.
what are the advantages and disadvantages of using a laser cutting robot?
Using a laser cutting robot offers several advantages, but it also comes with certain disadvantages. Here are some pros and cons of using a laser cutting robot:
Advantages/Pros:
1. Precision
Laser cutting robots provide high precision and accuracy, allowing for intricate and detailed cuts. They can cut complex shapes and designs with minimal distortion or errors, ensuring consistent results.

2. Speed and Efficiency
Laser cutting robots are capable of high-speed cutting, enabling efficient production and reducing manufacturing time. They can complete cuts quickly, resulting in increased productivity and throughput.
3. Versatility
Laser cutting robots can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, fabrics, and more. This versatility allows for diverse applications across different industries, providing flexibility in manufacturing processes.
4. Minimal Material Waste
Laser cutting robots have a narrow kerf width, which means they remove minimal material during the cutting process. This reduces material waste, making it a cost-effective solution for manufacturing.
5. Automation and Integration
Laser cutting robots can be integrated into automated production lines, allowing for seamless and continuous operation. They can be programmed and controlled to work in synchronization with other robotic systems, enhancing overall production efficiency.
6. Complex Geometries
Laser cutting robots can handle complex geometries, such as intricate curves, sharp corners, and patterns, which may be challenging to achieve with other cutting methods. This makes them suitable for applications that require intricate designs or complex components.
Disadvantages/Cons:
1. Cost
Laser cutting robots can be expensive to purchase and maintain. The initial investment cost, including the robot, laser source, control system, and safety measures, can be significant. Additionally, ongoing maintenance and periodic replacement of laser components can add to the overall cost. On the other hand productivity and efficiency of a laser cutting robot can compensate for all of these costs.
2. Safety Considerations
Laser cutting involves the use of high-powered lasers that can be potentially hazardous. Adequate safety measures, including laser enclosures, protective eyewear, and safety protocols, must be implemented to ensure the well-being of operators and compliance with safety standards. However, laser cutting robot offers certain safety advantages compared to human labor.
3. Material Limitations
While laser cutting robots can work with various materials, certain materials may not be suitable for laser cutting due to their composition or properties. For example, highly reflective or transparent materials may not be compatible with certain laser types.
4. Heat Effects
The laser cutting process generates heat, which can cause thermal effects on the material being cut. This may lead to material deformation, discoloration, or unwanted changes in the material properties, especially in heat-sensitive materials.
5. Complexity of Programming
Programming a laser cutting robot requires specific skills and knowledge. Setting up cutting parameters, defining paths, and optimizing cutting conditions can be complex and time-consuming. Skilled operators or programmers are often needed to ensure efficient and accurate operation.
For receiving programing services from T.S Group specialists you can call us.
6. Maintenance and Downtime
Laser cutting robots require regular maintenance, including cleaning, calibration, and replacing worn-out components. Any downtime for maintenance or repairs can impact production schedules and output. However, The efficiency and productivity provided by laser cutting robots are significantly higher compared to human labor, making them incomparable.
It’s important to consider these advantages and disadvantages when evaluating the suitability of a laser cutting robot for a specific application. The specific requirements, budget, and production needs of the industry should be taken into account to make an informed decision.
How many types of robotic laser cutting are there?
There are several types of robotic laser cutting methods, each with its own characteristics and applications. Here are some common types:
1. CO2 Laser Cutting:
CO2 laser cutting is one of the most widely used methods. It utilizes a high-powered CO2 laser beam to cut through various materials, including metals, plastics, and organic materials like wood and fabric.
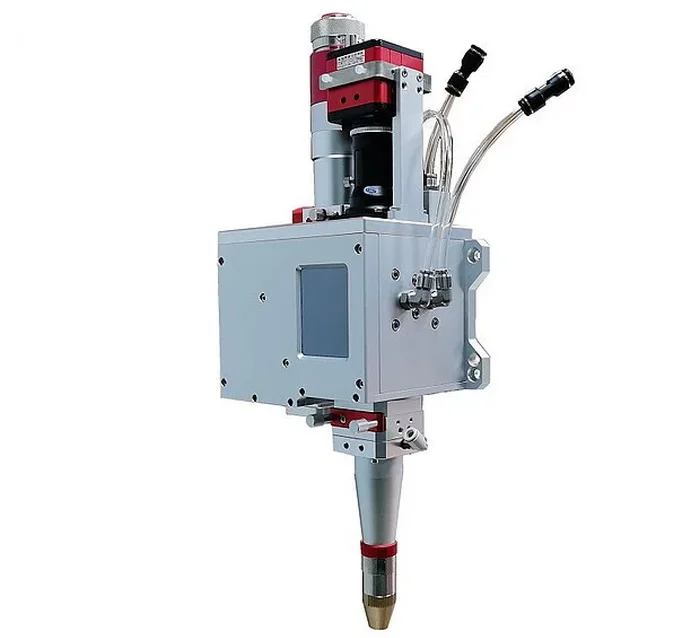

2. Fiber Laser Cutting
Fiber laser cutting employs a fiber laser source that generates a concentrated laser beam. It is particularly effective for cutting metals such as steel, aluminum, brass, and copper. Fiber lasers offer high cutting speeds and are known for their efficiency and precision.
3. Nd:YAG Laser Cutting
Nd:YAG (Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) laser cutting utilizes a solid-state laser with a crystal medium. It is commonly used for cutting thin metals and non-metals, as well as for applications that require high-precision cutting, such as in the electronics industry.
4. Excimer Laser Cutting
Excimer lasers use a combination of reactive gases to produce short-wavelength, ultraviolet laser beams. This type of laser cutting is primarily used for precise cutting of delicate materials, such as medical devices, electronic components, and microelectronics.
5. Pulsed Laser Cutting
Pulsed laser cutting involves delivering laser energy in short bursts or pulses. It is often used for materials that are difficult to cut with continuous-wave lasers, such as certain ceramics, composites, and heat-sensitive materials.
6. Hybrid Laser Cutting
Hybrid laser cutting combines laser cutting with other cutting methods, such as waterjet cutting or plasma cutting. This hybrid approach combines the benefits of both techniques, enabling efficient cutting of thick materials or materials with complex compositions.
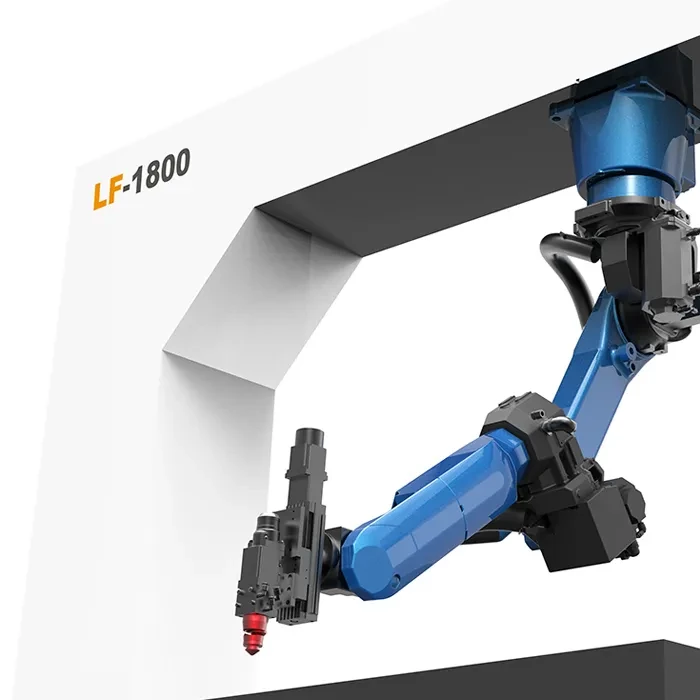

These are just a few examples of the types of robotic laser cutting methods available. The choice of method depends on the specific material to be cut, the desired precision, cutting speed, and other application requirements. Each type of laser cutting method has its own advantages and is suited for specific materials and applications.
what are the components of a laser cutting robot?
A laser cutting robot typically consists of several key components that work together to perform the cutting process. Here are the main components of a laser cutting robot:
1. Robot Arm
The robot arm is the mechanical structure of the robot that moves and positions the cutting tool. It typically consists of several articulated joints, allowing for precise movement in multiple axes.
2. End Effector
The end effector, also known as the cutting head or tool, is the part of the robot that holds and manipulates the laser cutting tool. It may include additional components such as a focusing lens, nozzle, and sensors for monitoring and controlling the cutting process.
3. Laser Source
The laser source is the device that generates the laser beam used for cutting. Different types of lasers, such as CO2, fiber, or Nd:YAG lasers, may be used depending on the specific cutting requirements and materials.
4. Beam Delivery System
The beam delivery system consists of optics and mirrors that guide the laser beam from the laser source to the cutting head. It ensures the laser beam is directed accurately and efficiently.
5. Control System
The control system is responsible for programming and controlling the robot’s movements and the laser cutting process. It may include software and hardware components for setting cutting parameters, defining cutting paths, and coordinating the robot’s actions.
6. Safety Measures
Laser cutting robots require various safety measures to protect operators and ensure safe operation. These may include laser enclosures or barriers, safety interlocks, emergency stop buttons, and laser safety protocols.
7. Workpiece Fixturing
Depending on the application, the laser cutting robot may incorporate workpiece fixturing systems to secure the material being cut. This ensures stability during the cutting process and accurate positioning of the workpiece.
8. Control Interface
The control interface allows operators or programmers to interact with the robot, set parameters, and monitor the cutting process. It can be a user-friendly graphical interface or a more advanced programming interface depending on the system.
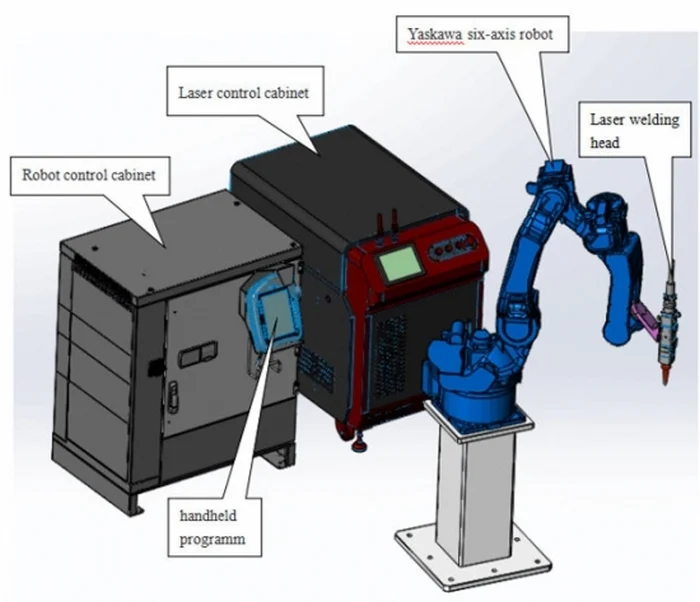
These are the fundamental components typically found in a laser cutting robot. However, specific configurations and additional components may vary depending on the manufacturer, model, and application requirements.
is laser cutting robot safer than human labor?
Laser cutting robots can offer certain safety advantages compared to human labor, but it’s important to implement proper safety measures and protocols to ensure a safe working environment. Here are some considerations:
1. Reduced Physical Hazards
Laser cutting robots can operate in hazardous environments without risking human operators’ safety. They can work in areas with high temperatures, fumes, or airborne particles, minimizing the risk of direct exposure to such hazards.
2. Minimal Contact with Cutting Process
Laser cutting robots are designed to keep human operators at a safe distance from the cutting process. The laser beam and cutting operations are typically enclosed within a protective enclosure or behind safety barriers. This reduces the risk of accidental contact with the laser beam or moving parts of the robot.
3. Automated Safety Systems
Laser cutting robots often have built-in safety systems, such as emergency stop buttons, laser safety interlocks, and motion detection sensors. These systems can halt the cutting process or shut down the robot in case of an emergency or when a safety breach is detected, enhancing overall safety.
4. Reduced Risk of Repetitive Motion Injuries
Repetitive motion injuries, such as strains or musculoskeletal disorders, can occur when human operators perform repetitive cutting tasks for extended periods. Laser cutting robots eliminate this risk, as they can operate continuously without fatigue or physical strain.
5. Safety Training and Compliance
Proper training and adherence to safety guidelines are essential when working with laser cutting robots. Operators should receive adequate training on laser safety protocols, machine operation, and emergency procedures. Compliance with safety regulations and standards, such as laser safety standards (e.g., ANSI Z136.1) and local workplace safety regulations, is crucial to ensure a safe working environment.
Considerations for using a laser cutting robot in terms of safety
However, it’s important to note that laser cutting robots still pose certain safety considerations:
1. Laser Beam Hazards
Laser beams used in laser cutting can be harmful to the eyes and skin. Operators and maintenance personnel must follow strict laser safety guidelines, including wearing appropriate protective eyewear and clothing, to avoid direct exposure to the laser beam.
2. Maintenance and Servicing
During maintenance or servicing of laser cutting robots, there can be potential hazards related to electrical systems, moving parts, and the laser source itself. Proper lockout/tagout procedures and adherence to maintenance protocols are necessary to ensure safe servicing practices.
3. Operator Error and System Malfunctions
While laser cutting robots can enhance safety through automation, operator error or system malfunctions can still occur. Human involvement in programming, setup, and operation introduces the possibility of errors. Regular system inspections, maintenance, and operator vigilance are essential to mitigate these risks.
Overall, when proper safety measures are in place and followed, laser cutting robots can provide a safer working environment compared to certain manual cutting processes. However, it’s crucial to prioritize safety training, implement appropriate safety protocols, and conduct regular safety assessments to ensure a safe working environment when working with laser cutting robots.
is the laser cutting robot more efficient than human labor?
In many cases, a laser cutting robot can offer greater efficiency compared to human labor. Here are some factors to consider:
Speed and Productivity: Laser cutting robots can operate at high speeds, resulting in faster production rates compared to manual cutting methods. They can perform repetitive cutting tasks with consistent speed and precision, leading to increased productivity and throughput.
Accuracy and Consistency: Laser cutting robots provide precise and consistent cuts, ensuring uniformity in the produced parts or components. Human operators may have variations in cutting quality due to factors such as fatigue, skill level, and concentration. Robots eliminate these inconsistencies, leading to higher accuracy and a reduction in rework or scrap.
Continuous Operation: Laser cutting robots can work continuously without experiencing fatigue or the need for breaks, unlike human operators. They can operate 24/7, allowing for non-stop production and maximizing efficiency.
Complex Geometries and Designs: Laser cutting robots excel at cutting complex shapes, intricate designs, and precise patterns. They can execute intricate cuts with ease, which may be time-consuming or challenging for humans to achieve. This capability is particularly beneficial in industries where intricate or customized designs are required.
Material Waste Reduction: Laser cutting robots produce minimal material waste due to their narrow kerf width and precise cutting ability. They optimize material utilization, reducing costs associated with wasted material.
Automation and Integration: Laser cutting robots can be integrated into automated production lines, allowing for seamless workflow and synchronization with other manufacturing processes. This integration enhances overall production efficiency and reduces manual labor requirements.
Considerations for using a laser cutting robot in terms of efficiency
However, it’s important to note that there are certain cases where human labor may still be preferred over laser cutting robots. For example:
1. Small-Scale or Customized Production
In situations where the production volume is low or the customization requirements are frequent, human labor may be more flexible and cost-effective. Humans can quickly adapt to changing requirements and perform manual adjustments or fine-tuning that robots may struggle with.
2. Complex Setups and Non-Repetitive Tasks
For tasks that involve complex setups, irregular shapes, or non-repetitive cutting patterns, human operators may have an advantage. They can quickly adapt and make adjustments as needed, whereas reprogramming a laser cutting robot for each unique task may be time-consuming.
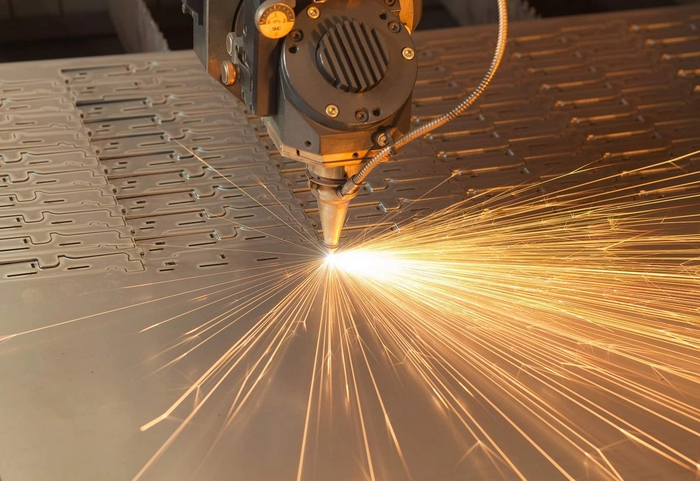

3. Skill-Based Judgment
Certain cutting tasks may require human judgment and expertise, especially when dealing with delicate or sensitive materials. Human operators can provide real-time adjustments and decision-making based on their experience and knowledge.
In summary, laser cutting robots generally offer higher efficiency, speed, and accuracy for repetitive cutting tasks, especially in high-volume production scenarios. However, there are situations where human labor may still be preferred due to flexibility, adaptability, and skill-based judgment requirements. The specific needs of the application and production environment should be carefully considered when deciding between laser cutting robots and human labor.
Conclusion
a laser cutting robot is a powerful tool that offers numerous advantages in various industrial applications. Its precision, speed, versatility, and automation capabilities make it a highly efficient option for cutting a wide range of materials. Laser cutting robots can deliver intricate designs, complex geometries, and consistent results while minimizing material waste. They integrate seamlessly into automated production lines, enhancing overall productivity and throughput.
Overall, laser cutting robots have revolutionized the manufacturing industry by offering increased efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. Their ability to perform repetitive cutting tasks at high speeds with precision makes them an invaluable tool in various industries, ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and textiles. As technology continues to advance, laser cutting robots are expected to play an even greater role in shaping the future of manufacturing.
Is T.S.Group Yaskawa’s representative?
In fact, no company currently represents Yaskawa in Iran. Some companies misuse this title and introduce themselves as Yaskawa’s representative in Iran to attract customers’ attention. For more information, please read the article “Yaskawa’s representative in Iran”.
TS Group does not introduce itself as Yaskawa’s representative in Iran, but our relationship with Yaskawa is direct and we receive technical support directly from Yaskawa.

